Morning, long-lifers. Here’s what’s new:
Exergaming boosts brain health in memory-impaired adults - proving that swinging a virtual tennis racket may actually sharpen your recall instead of just your forehand.
At this rate, Wii Sports might end up in the neurology ward right next to Sudoku.
Don’t keep longer. a secret - share it with your friends!
This week in longevity:
🥗 Two days of junk food clouds memory
🦠 Genes that guard the gut
🧩 Aging protein linked to memory loss
🤖 AI predicts health timelines
💊 Pressure calculator personalizes drug response
Plus, more longevity breakthroughs.
Read time: 5 minutes
THIS WEEK IN LONGEVITY
🥗 Eating for 12 hours may help you live longer

Source: Midjourney | longer.
A new U.S. study suggests that the sweet spot for daily eating is around 11–12 hours. Shorter or longer eating windows were linked to a higher risk of early death. Think of it like Goldilocks’ porridge: too short or too long may backfire, but just right could keep you healthier for longer.
What to know:
Study size: Researchers tracked 33,052 American adults over a median of 8 years, documenting more than 4,000 deaths.
Optimal window: Eating across 11–12 hours daily was linked to the lowest mortality risk.
Too short: Eating in under 8 hours increased the risk of death by 34%, with older adults and men seeing the biggest cardiovascular risks.
Too long: Eating for 15+ hours showed a 25% higher risk, though results were weaker and mostly seen in White participants.
Why extremes hurt: Very short windows can mean missing nutrients or calories, while very long ones often involve late-night eating that disrupts circadian rhythms (your body’s internal clock).
Why it matters: This study suggests that eating all your meals in a super-tight fasting window may not be the longevity hack people hoped. Your body seems to prefer balance over extremes. Basically, moderation even applies to intermittent fasting.
What this means in practice: Aim to finish eating within an 11–12-hour span most days — like 8 a.m. to 8 p.m. or 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Skip the ultra-restrictive or all-day grazing routines. Your heart, metabolism, and future self will likely thank you.
MADE POSSIBLE BY VIOME
🧬 Your body’s not guessing - so why are your supplements?

Source: Viome
Viome’s Full Body Intelligence Test looks at your microbiome, cellular health, and biological age to show what’s really going on inside.
Then it builds personalized supplements based on your results - only what your body needs, nothing extra.
Better sleep. Better energy. Better digestion.
Trusted by 500,000+ and shipped straight to your door.
🕹️ Video games that exercise your body may also protect your brain

Source: Midjourney | longer.
A study found that “exergaming” — video games that make you move — may boost brain health in people with mild cognitive impairment (early memory problems that can precede dementia). After 12 weeks, players showed brain changes linked to better memory. Turns out, a virtual tennis match might also train your hippocampus.
What to know:
What exergaming is: Video games or virtual sports that require real physical activity, blending movement and play.
Study details: 41 adults with mild cognitive impairment were assigned either exergame plus breathing training or usual care for 12 weeks.
Brain benefits: MRI scans showed growth in gray matter (brain cells) in the hippocampus, a key memory hub, and better integrity in white matter (the brain’s wiring).
Memory gains: Participants improved in immediate and delayed verbal recall, while the control group declined.
Caveats: Small sample size, short study length, and results may not apply to all types of cognitive impairment.
Why it matters: Exergaming may offer a safe, engaging way to slow memory decline, especially for people worried about dementia. The brain seems to like workouts that mix sweat and play.
What this means in practice: Add some movement-based gaming to your routine, like Wii tennis, VR boxing, or dance games. If exercise feels like play, you’ll keep doing it and your brain may quietly cash in the benefits.
💡 Want to break down a research article? Try this prompt in ChatGPT:
“Explain this in plain language. Avoid science terms. Keep it under 5 sentences. Then give 5 takeaways based only on this summary—no extra info or guesses: [Paste the article here]”
MONEY MOVES IN LONGEVITY
💰 Diana Health raises $55M Series C, expands hospital partnerships; midwives step up as OB units shut down.
💰 Bio Protocol raises $6.9M to launch AI-native DeSci platform; first agent mints 1K+ hypotheses onchain.
IN THE SPOTLIGHT

Source: Midjourney | longer.
1. Two days of junk food can cloud memory
Mice on a Western-style high-fat diet lost hippocampal glucose within 48 hours. This over-activated inhibitory neurons and blocked memory formation. Returning to normal food restored memory. Turns out, the brain has a sweet tooth too, and it notices fast when it’s not being fed.
2. Genes that guard the gut
Scientists found that alpha-defensin genes help shape the microbiome and protect against obesity and diabetes. Mice lacking these proteins developed insulin resistance, while supplementation improved health. Yet the same treatment harmed mice already making enough, showing that gut fixes may need to be as personal as fingerprints.
3. Aging protein found in the brain
Researchers discovered that Menin, a protein in the hypothalamus, declines with age. This sparks inflammation and lowers D-serine, harming memory, skin, and bone health in mice. Restoring Menin or supplementing with D-serine reversed these problems, hinting that aging may be partly negotiable after all.
THE NEXT BIG THING
AI takes a crack at your health timeline

Source: Midjourney | longer.
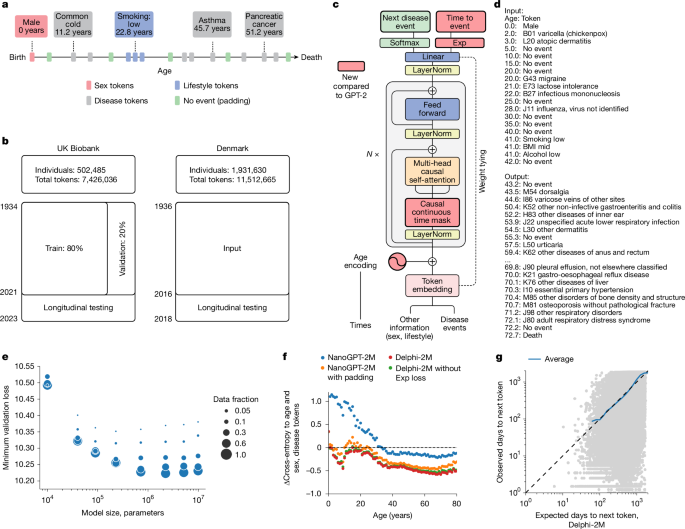
A new generative AI model from European and Danish researchers can estimate risks and timing for over 1,000 conditions.
It learns from medical histories like a language model—using the order and spacing of diagnoses, lifestyle factors and demographics to forecast likely health paths. The goal: shift healthcare from treating illness to anticipating and preventing it.
Early step toward preventive medicine or overreach of prediction?
WHAT ELSE YOU SHOULD KNOW THIS WEEK

Source: Midjourney | longer.
🧠 Tablet Test: A new 11-minute iPad test called BioCog detected early Alzheimer’s with 85–90% accuracy in over 400 patients, outperforming doctors’ judgment and standard memory tests.
💊 Pressure Tool: Scientists at The George Institute built a calculator using data from nearly 500 trials to predict exactly how much blood pressure drugs lower readings. It could guide faster, tailored treatments for 1.3 billion people worldwide.
💉 Longevity Shift: At a major aging science meeting in Copenhagen, Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk called GLP-1 drugs “longevity medicines” for the first time. This bold rebranding signals Big Pharma’s entry into aging as a treatment target.
🧬 Brain Reboot: Retro Biosciences, backed by OpenAI’s Sam Altman, is starting a trial of a drug designed to reverse Alzheimer’s using cellular reprogramming. With $1 billion in funding, the startup aims to extend healthy life by 10 years.
🌍 Trust First: The Lifespan Research Institute just launched the Public Longevity Group to boost acceptance of aging therapies. Its $100K crowdfunding campaign will build tools to track and strengthen public trust in longevity science.
WHAT WE’RE BOOKMARKING
📱 Social
🎧 Podcasts
📰 Articles
⚙️ Tools to Try
Thanks for reading.
What did you think of this week’s newsletter?
See you in the next issue.