
Morning, long-lifers. Here’s what’s new:
Changing how you point your toes while walking may cut knee pain as well as ibuprofen - finally, a drug-free excuse to walk funny on purpose.
Orthopedic fashion week just got a whole lot weirder.
Don’t keep longer. a secret - share it with your friends!
This week in longevity:
🥗 MIND diet protects brain’s memory hub
🐟 Omega-3s may shield women from Alzheimer’s
🔋 Calorie restriction shrinks organs and metabolism
🧪 Lithium reverses memory loss in mice
🦴 Nanoparticles restore bone strength in old mice
Plus, more longevity breakthroughs.
Read time: 5 minutes
THIS WEEK IN LONGEVITY
🚶 Small walking tweak may ease knee pain

Source: Midjourney | longer.
Changing the angle of your foot while walking might be as effective as popping an ibuprofen, according to new research on knee osteoarthritis (OA). In a year-long trial, people who slightly adjusted their foot angle saw less pain and slower cartilage breakdown. Basically: the way you walk today could change how your knees feel years from now.
What to know:
The condition: Osteoarthritis (OA) happens when cartilage (the cushioning inside joints) wears down, often causing pain and stiffness. It affects about 1 in 7 Americans, mostly in the knees.
The experiment: 68 people with mild to moderate knee OA were taught to angle their feet slightly inward or outward (by 5–10 degrees) based on computer gait analysis.
The results: Those who adjusted their foot angle cut joint stress by 4% and reported pain relief equal to over-the-counter pain meds. Those who didn’t change increased joint stress by 3%.
Long-term benefit: MRI scans showed slower cartilage degeneration in the “foot-angle” group compared with those who just walked more.
Why it works: Small shifts redistribute loading (pressure) on the knee, easing stress on the inner joint — where OA damage is usually worst.
Why it’s important: Knee replacements are common, but the earlier you get one, the higher the chance you’ll need a second. A simple foot-angle tweak could buy your knees more time — free medicine hidden in the way you walk.
What this means in practice: Researchers adjusted each person’s foot slightly inward or outward (about 5–10°) to reduce knee stress. Right now this requires gait labs, but simple motion-tracking tools may soon let clinics do it quickly.
MADE POSSIBLE BY VIOME
🧬 Your body’s not guessing - so why are your supplements?

Source: Viome
Viome’s Full Body Intelligence Test looks at your microbiome, cellular health, and biological age to show what’s really going on inside.
Then it builds personalized supplements based on your results - only what your body needs, nothing extra.
Better sleep. Better energy. Better digestion.
Now through Sept. 2: $100 off for Labor Day (no code needed).
Trusted by 500,000+ and shipped straight to your door.
🥗 MIND diet linked to brain protection

Source: Midjourney | longer.
Eating in line with the MIND diet — a mix of the Mediterranean and DASH diets — has long been tied to lower dementia risk. A new study suggests one reason why: it may protect the hippocampus (the brain’s memory hub) from a type of damage called hippocampal sclerosis. Turns out broccoli and salmon might be doing more than keeping your heart healthy.
What to know:
The diet: MIND stands for Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay. It emphasizes vegetables, whole grains, fish, and poultry, while limiting dairy, red meat, and fried food.
The study: Researchers analyzed brain tissue from 809 people whose diets had been tracked for years before death.
The finding: People who stuck most closely to the MIND diet were less likely to show hippocampal sclerosis (cell death in the hippocampus, the brain’s memory and learning center).
Why it matters biologically: Damage to the hippocampus is strongly linked to dementia, so protecting this region may explain part of the diet’s effect.
The mechanism: The foods in the MIND diet are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that may shield neurons from stress and damage.
Why it’s important: Dementia has no cure, so protecting the brain before problems start is the best defense we have. A plate full of leafy greens and fish might be doing quiet repair work where it counts most.
What this means in practice: The MIND diet is not a new prescription but a pattern of eating. More vegetables, berries, nuts, whole grains, fish, and poultry, and fewer fried foods and red meats, were what set the lowest-risk group apart.
💡 Want to break down a research article? Try this prompt in ChatGPT:
“Explain this in plain language. Avoid science terms. Keep it under 5 sentences. Then give 5 takeaways based only on this summary—no extra info or guesses: [Paste the article here]”
MONEY MOVES IN LONGEVITY
💰 Eight Sleep raises $100m to push beds into health, turning nightly rest into a real-time checkup.
💰 Radical Life Extension raises €300K for anti-aging research, keeps Alicante labs buzzing with bold science.
💰 Morrow launches in Singapore with $156m investment; longevity goes from lab to lifestyle under one roof.
IN THE SPOTLIGHT

Source: Midjourney | longer.
1. Calorie restriction shrinks organs and metabolism
A 2-year trial found that cutting calories by 25% reduced fat, muscle, and even organ size. Energy use dropped more than weight loss alone explained. Your body doesn’t just slim down, it powers down too, a thrifty survival trick that makes maintaining weight loss harder than losing it.
2. Omega-3s may shield women from Alzheimer’s
A study of 841 people found women with Alzheimer’s had far lower levels of omega-3-rich lipids, but men showed no such link. Unsaturated fats tracked with better brain health. Women make up two-thirds of cases, and for them fish oil may be more than brain food, it could be brain armor.
3. Targeting brain iron protein reverses memory decline in old mice
Researchers found that reducing levels of Ftl1, a protein tied to brain iron buildup, improved learning and memory in aged mice. By easing iron overload, a known driver of oxidative stress and neurodegeneration, this approach hints at a future therapy to slow age-related cognitive decline.
THE NEXT BIG THING
First blood-free biomarker patch
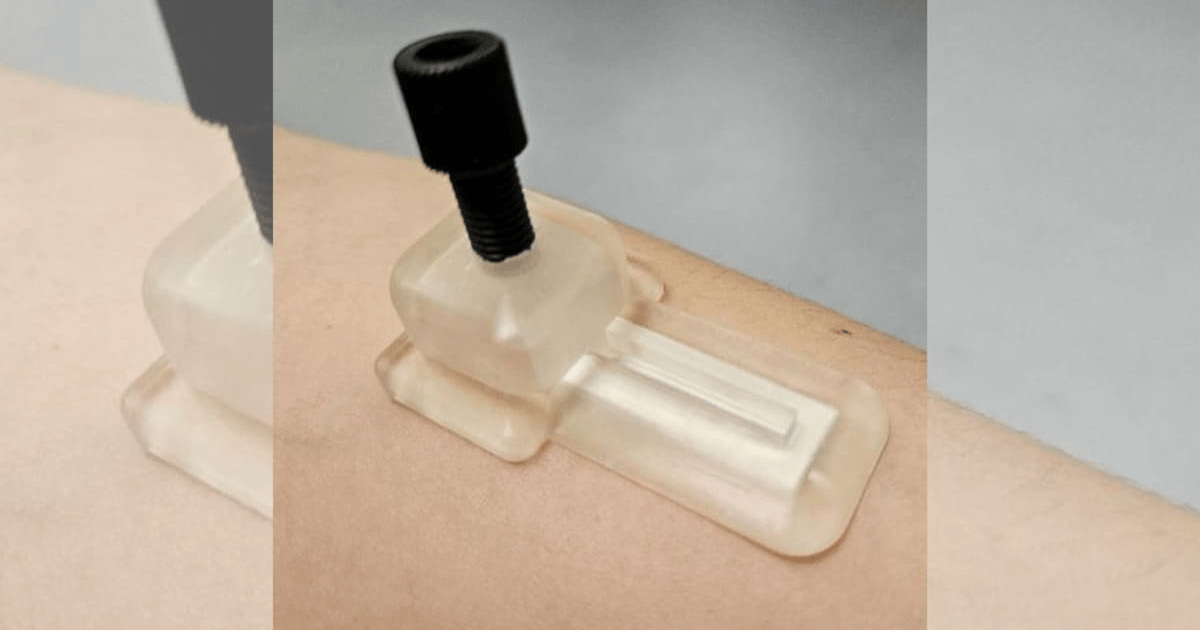
Source: Michael Daniele, NC State University
Researchers just unveiled a microneedle patch that collects health biomarkers without blood, batteries, or external devices.
The patch draws interstitial fluid through microneedles, stores it on paper strips for up to 24 hours, and enables easy monitoring of stress, hormones, and other biomarkers. The goal: painless, low-cost, at-home health tracking without repeated blood draws.
Future of diagnostics or limited to niche use?
WHAT ELSE YOU SHOULD KNOW THIS WEEK
Source: Midjourney | longer.
🧪 Lithium Lifeline: Harvard scientists found tiny doses of lithium, a natural mineral used in mood medicine, reversed memory loss in Alzheimer’s-prone mice. The treatment cleared plaques, restored learning, and showed no side effects.
🧩 Brain Switch: UC San Diego scientists found a tiny piece of DNA that shapes how brain cells grow. It helps make more neurons, boosting memory and flexible thinking.
❤️ Aging Heart: A new review explains how aging stiffens blood vessels, weakens the heart, and sparks “inflammaging” (chronic low-grade inflammation). Scientists suggest targeting oxidative stress and inflammation to slow this decline.
🦴 Bone Boost: Chinese researchers used tiny mitochondria-targeting nanoparticles to restore bone strength in old mice. After 10 weeks, aged bones looked young again and regained full strength.
😴 Sleep Shield: Seragon launched Enlivien, a supplement that fights cell damage from poor sleep. Inspired by Harvard research, it targets gut stress to slow aging and boost resilience.
WHAT WE’RE BOOKMARKING
📱 Social
🎧 Podcasts
📰 Articles
⚙️ Tools to Try
Thanks for reading.
What did you think of this week’s newsletter?
See you in the next issue.




